Android External Storage Support: Mount Service Architecture
Introduction.
We have already seen in
the previous tutorial that the vold service talks to the MountService which is
responsible for actually initiating commands from the userspace to
mount,unmount,create,remove
different volumes.
Let us spend sometime to
understand more on this.
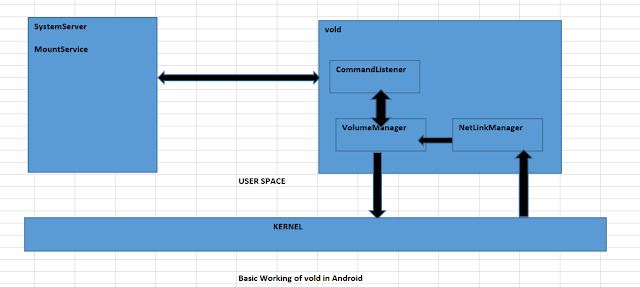
The relationship between
the command message, MountService, Vold, and Kernel is shown in the following
figure.
Vold receives the kernel uevent message through the Netlink messages and sends them to the MountService through the socket method and receives the MountService commands in real time.
We
have seen earlier that vold process
1.
CommandListener module creates a socket listener thread at
startup.
2.
The thread is used to listen to MountServcie's connection and
receives the command message sent by the MountService to Vold.
The
MountService needs to receive the uevent message from the kernel. It must also
create a socket monitor thread. The socket monitor thread will be explained in
detail later.
Android
MountService.
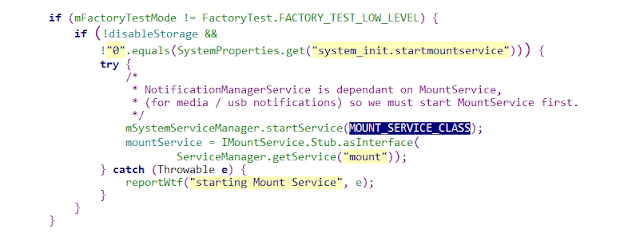
MountService is one of Android's Java services. It is created and registered in ServiceManager
during the second phase of SystemServer process startup.
Let
us see the MountService creation and registration process.
If you see above, You will see that MountService is also a singleton as we would like only one instance running in the systemserver only.
Before
we move further let us spend sometime and look at the file storage_list.xml.
MountService
reads the xml file and constructs a
StorageVolume object according to the storage device parameters and stores all
the constructed StorageVolume objects in the list mVolumes which we will visit
later.
Let
us see some important steps during the MountService initialization.
Create
a Handler for the MountService worker thread with a message loop.
Create
an ObbActionHandler for the MountService worker.
Create
the connection to vold with a maximum queue of twice the amount of containers
we'd ever expect to have. This keeps an "asec list" from blocking a
thread repeatedly.
Create
and start a socket connection listening thread using NativeDaemonConnector.
Register for ADDED and REMOVED intents.
Add ourselves to the watchdog monitors if they are available.
MountService
service model.
We
can see that the SystemServer main thread starts the MountService service. When
the service starts, a MountService worker thread with a message loop is created
to handle the messages dispatched by the MountServiceHandle and
ObbActionHandler; at the same time, a service for connecting the Vold is
created.
Before
entering the closed loop, the thread creates a NativeDaemonConnector.CallbackHandler
thread with a message loop, which is used to process the uevent event message
sent by the native layer Vold process.
MountService
thread creation.
The different messages which are handled by the MountService.
MountService sending command to vold.
Vold
acts as a storage device control center and needs to receive operation commands
from the upper MountService.
The
communication between MountService which resides in the SystemServer process
and Vold as two different processes uses socket communication.
While
analyzing the vold process in the previous tutorial we have seen the CommandListener
module that initiates a socket listener thread to specifically receive
connection requests from the upper-level MountService.
At
the MountService side the NativeDaemonConnector socket connection thread is
also started for looping connection to the server to ensure that the connection
is not interrupted.
When
the connection to Vold is successful, the loop reads data from the server.
The
MountService sends commands to the Vold in a specified format.
Let
us take an example of the mount command.
Read the responses and process them using NativeDaemonEvent and we are done.
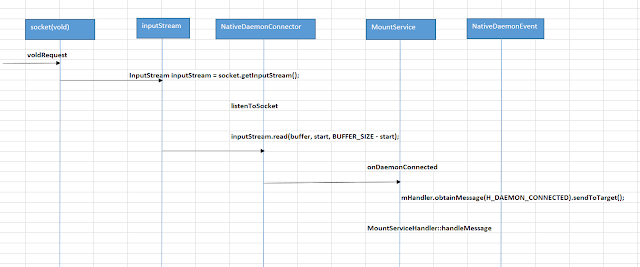
vold sending messages to MountService.
We
saw above how the MountService interacts with vold when it receives a user
command, However we would also like know how does the vold on getting the
ueventd Netlink messages inform MountService.
Let
us see a basic workflow and then directly jump into source code.
Start
a looper and listen to the socket.
Read the data obtained on the socket.
Send
the data for further processing using the connected Daemon.
Obtain
the message in the Mountservice and handle the message.
We
already know that some apps/services etc would have registered to the MountServiceListener
and MountService needs to update all of them.
We
also saw the different message handling in the MountService:: handleMessage function
earlier , Let us revisit.
Finally
the required function gets called which handles the daemon connected event.
Let
us see how can some entity register to the MountService and listens to the
events or updates on the external storage.
It
is accomplished using the StorageManager class and registering to its listener.
Let
us see how using the UsbStorageActivity class.
Hope,
That the basic idea of VolumeService gives us quite an insight of how the
external storage [sdcard/USB drive] are managed in the Android system.










































Now, MountService is deprecated, Instead StorageManagerService is used along with aidl binder transaction
ReplyDelete